electrical:12v:parallel_serial
parallel-serial
Electrical components like batteries and solar panels can be used independently or combined. If combined, they are connected in series or in parallel.1) For the following examples we will consider two items – batteries, solar panels, etc.
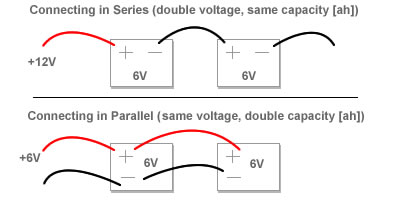
Series connections double the voltage while the current (or capacity in Ah when dealing with batteries) remains unchanged.
- common example: 2 6v, 200Ah golf cart batteries in series = a 12v, 200Ah battery bank.2). This is a recommended configuration.
- less common example: 2 12v, 90Ah batteries in series = a 24v, 90Ah battery bank.
Parallel connections double the current while the voltage remains unchanged.
- common example: 2 12v, 90Ah batteries in parallel = a 12v, 180Ah battery bank.
Wide parallel configurations (like 4P) are difficult to charge/discharge evenly without exotic cable configurations.
notation
When discussing multi-battery banks it is common to describe the electrical layout with a particular notation.
p = parallel
s = series
Examples:
- 1p1s - a single battery
- 1p2s - two batteries in series, as one finds in the common 2x6v GC battery setup
- 2p1s - two batteries in parallel
- 2p2s - two sets of batteries in parallel linked in series as one finds in higher-capacity GC-based setups
electrical/12v/parallel_serial.txt · Last modified: 2025/12/24 22:58 (external edit)