This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Words of Wisdom: “if [you're] the type to park the rig, let the batteries die and boost them for the next time [you're] using it, get the cheapest batteries out there. [You're] killing them anyway.” – twinboat1)
Deep cycle batteries
Deep cycle batteries are batteries which are designed to have an extreme depth of discharge (DoD) between full charges. For longest life, lead-acid chemistries (flooded or sealed/AGM) are discharged down to about 50% State of Charge (SoC) and then recharged fully every day. Similarly, Lithium-chemistry batteries can be discharged to about 20% SoC, and do not need to be fully charged every day. They are very tolerant of partial charging.
In campervan scenarios the batteries hit their lowest SoC just before dawn and are fully charged sometime before sunset (the earlier the better).
Batteries can be charged with a smart or three-stage charger for optimal performance and longevity.
Note: This article assumes useage of 12v lead chemistries. If you're using Lithium, this information is not as applicable. Please see the Drop-in Lithium batteries article, or for the more industrious the Lithium Battery DIY thread page
Popular Deep-Cycle Lead batteries
6v golf cart batteries are the gold standard for a true deep-cycle lead chemistry battery. They were designed for deep cycle use, and with proper maintenance can last for years. They are extremely heavy and two batteries are generally wired in series to make a 12v bank.
Words of Wisdom: “The worst 6v GC-2 battery is still a better deep cycle battery than 99.98% of flooded 12v batteries sold in deep cycle applications.” – SternWake2)
This is “The short list” of Golf Cart battery makes & models that have proven popular and reliable over the years.
Trojan T-105
The Trojan T-105 RE is the canonical deep cycle battery.
Trojan recommends a 14.8v absorption setpoint.
Other GC-2 batteries
Cheaper and easily exchanged batteries are often recommended as “learner batteries” that will be destroyed by newbie error.3)
These batteries:
“are very popular on RV forums if nothing else for the ability to be returned all over the country. Trojans for as wonderful as they are, can be ruined just as easily as any GC battery.” jimindenver4)
Deka GC-2 can be sourced from Batteries Plus.5)
Costco GC-2 (Enterprise, Interstate, etc) are about half the price of Trojans.6)
Energizer GC-2 are sold at Sam's Club. They are made by various manufacturers:
Energizer gc-2s could be made by johnson controls or USbattery or Exide or Eastpenn/deka or perhaps others depending on where they decided to source them at that time, and where in the country they are located at purchase. I would not want GC-2s made by johnson controls or exide. SternWake7)
Duracell GC-2 are a Deka brand made by East Penn.8) They can be sourced at Batteries Plus and Sam's Club.
The USbattery GC-2 can be sourced from Batteries Plus.9)
NAPA carries a GC-2 made by Exide.10)
popular lithium batteries
See this listing on the drop-in lithium page.
Battery Health
DoD vs. duty cycles
lead chemistries
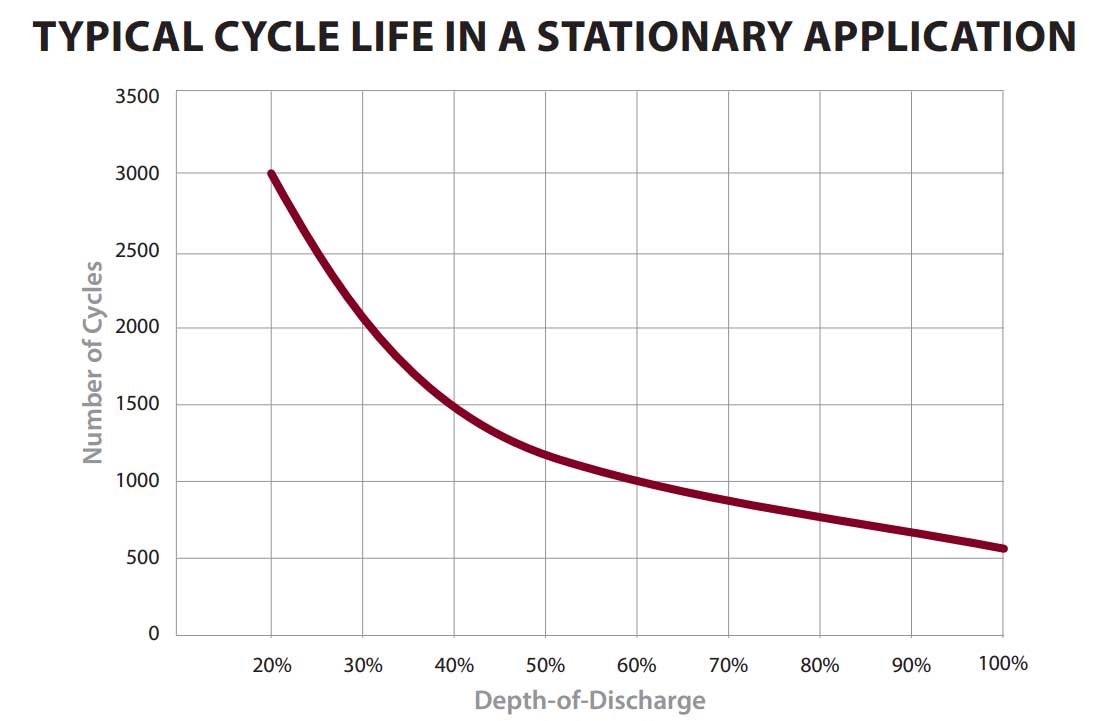 Lead deep cycle batteries are most commonly discharged to 50% DoD11), but can be discharged to other levels with radical results in the life of the battery.
Lead deep cycle batteries are most commonly discharged to 50% DoD11), but can be discharged to other levels with radical results in the life of the battery.
On this graph from Trojan we see the following pattern:
- discharging to 50% DoD14) daily will yield ~1200 duty cycles (~3.3 years of daily use, ~$0.21/KWh)
- discharging to 80% DoD15) daily will yield ~500 duty cycles (~1.4 years of daily use, ~$0.26/KWh)
Since drawing down 20% vs. 50% is the same cost over time it might be best to aim for 20% DoD and cycle to 50% DoD when needed. This would decrease the number of battery replacements while getting maximum use.
Drawing down to 80% DoD consistently is 24% more expensive and requires much more replacement effort. [Those things are heavy! – Secessus] Occasional/emergency drops to 80% DoD followed by full charging the next day will not inflict meaningful damage to the battery.
lithium chemistries
Lithium cycle ratings are typically assume:
- 80% DoD
- C/5 charge rates
- at human-comfortable temperatures
Cycles may be increased by avoiding high voltages, high currents, and avoiding both very low and very high states of charge.
Battery Lifespan
Batteries are typically replaced when they can no longer provide 80% of their rated capacity. This requires fully charging, then discharging at the 20-hr rate (C/20) until the battery is depleted. This is impractical with house batteries that are in actual use.
Because of this, we use indirect methods to assess battery health.
Quickly rising to absorption voltage during bulk and never seeing tail current drop down to previous levels are good indicators that the battery is in a declined or seriously declining state. mainesail16)
Tail current (aka endAmps, finishing amps) for healthy lead batteries is typically between C/200 and C/100 (0.5A to 1.0A at Vabs for per 100Ah of capacity). If tail current cannot get down to (C/50) 2A we can assume there is trouble on the horizon.
The rise to absorption voltage is rarely useful in the field since:
- solar charging alone is rarely able to hit charge current maximums
- alternator charging is rarely able to hit Vabs
People charging off larger DC-DC, shore power, or generators may be able gauge the speed at which the bank comes up to Vabs.
Premature failure
Lead batteries tend to lose capacity very gradually over time, and are typically replaced when they only have 80% of their rated capacity. If a dying battery still meets your needs feel free to use it until it croaks.
Lead batteries can fail prematurely from abuse and/or undercharging (usually gradual), or physical failure like cells shorting out (usually sudden). Shorted batteries will tend to overheat when charged/discharged.
On FLAs, the definitive way to diagnose a shorted cell is to disconnect the battery and apply a reasonably heavy load (say, C/2 or so). Electrolyte in the shorted cell, if one is present, will boil.19)
Manufacturers
Each manufacturer also has their own in-house brand, e.g. Delco for Johnson Controls and Deka for East Penn. Exide and US Battery use their corporate name for their battery brand as well. Trojan sells under the Trojan, Trillium, Reliant and Ranger brand names and Concorde sells under the Concorde and Lifeline brand names…. [Interstate is a label, not a manufacturer]… The 4 big US battery makers offer a couple price and quality tiers for their customers to choose from, but generally batteries with the same specs (AH/RC, CCA, and BCI case size) will be essentially identical. Warranty, MSRP, etc. is set by the selling brand and may differ, but the physical product is the same. – Gary RVRoamer20)
Interstate batteries made by US Battery have “U” prefixes.21)
See also this archived PDF that attempted to document who makes what battery.
Types of Lead batteries
Generally speaking, lead batteries fall into three broad groups
- starter - relatively little lead, but thin and spongey, calcium-doped22) plates make a huge surface area for massive currents involved with starting the engine and immediately recharging from alternator. The addition of Calcium decreases internal resistance, increases the outgassing voltage23) point24), decreases self-discharge, but makes the plates more likely to be damaged by overcharging. 25)
- deep cycle - lots of lead formed into thick, smooth antimony-doped plates. Can move less current but can do so for a longer time and can tolerate deeper discharge. This comes at the cost of increased water loss and self-discharge rates. Deep cycle batteries prefer to be floated constantly after charging.
- hybrid/marine - plates tend to have middling thickness. They may have calcium-doped negative plates and antimony-doped negative plates.26)
FLA - Flooded Lead Acid
The most common deep cycle battery is flooded lead acid (FLA). They are least expensive in the long run but do require checking/refilling the cells with distilled water occasionally.
Common setpoints (check your manufacturer's recommendation):
- charge C/10 to C/527)
- Vfloat 13.2v when not deeply cycled; 13.8v when cycled daily
- Vabs 14.7v - 14.8v
VRLA - Valve Regulated Lead Acid
Words of Wisdom: “Generally, gel and AGM batteries have about 20% less capacity, cost about two times more, and have a shorter cycle life than comparable flooded lead acid batteries.” – Trojan28)
Valve Regulated Lead Acid batteries have the same chemistry as FLA but
- the battery case is sealed (with overpressure safety valve)
- the electrolyte is stabilized so it does not slosh. The electrolyte can be gelatinized or embedded in an absorbant material.29)
These two features combine to make a battery that can be mounted in positions other than upright and does not require the regular addition of water.
AGM
Note: High quality AGM makers include “Odyssey, Lifeline, Northstar, Fullriver, Rolls and Firefly”.30)
This type of VRLA battery stabilizes the electrolyte in an Absorbent fiberGlass Mat (AGM).
- PRO
- able to charge/discharge huge amounts of current
- can be mounted in odd positions, including upside down
- generally maintenance-free which can be a benefit if mounted in inaccessible areas
- no outgassing under normal conditions
- CON
- generally double the cost of FLA for about 20% less capacity31)
- Premium AGM need much more charging current than flooded, and it may be more than solar-only setups can provide.32) The charging rate given by Lifeline, a respected AGM manufacturer, is at least C/533) or battery life will be affected. They also say it is ok to charge up to 5C34) (!).35) Odyssey specifies C/2.5 charging rates for their batteries.36)37)
- even cheap AGM require more current than flooded: minimum C/5, max C/3.(20A-33A per 100Ah of battery capacity).
- fully charged AGM are slightly lower voltage than FLA38) (12.6 vs 12.7).
- outgassing is less likely but still need to be vented39)
Common setpoints (check your manufacturer's recommendation):
- charge with greater current like C/3
- Vfloat 13.2v when not deeply cycled; 13.8v when cycled daily
- Vabs 14.6v - 14.7v40)
Also see
- this archived test of deep cycle AGM by Practical Sailor magazine
Historical note: the original use for AGM was for long-term stationary floating on shore power for backup/UPS purposes, as one finds in industrial backups or in the bases of cell towers. In long-term stationary use the liquid electrolyte in flooded batteries can stratify, causing degradation. The electrolyte in AGM41) types cannot move freely and so will not stratify. Telcos and other industries typically replace the batteries after X years on float duty and sell them on the surplus market. They are not made for frequent cycling but still may represent a good value.
Gel cell
This type of VRLA battery gelatinizes the electrolyte with SiO2 (silicon dioxide) to stabilize it. While renowned for their exceptional duty cycle life, they are rarely used in campers due to cost, limited charging max similar to flooded42), and sensitivity to overvoltage.
“Lead crystal” batteries may actually be gel, since they claim the electrolyte is made of SiO2.43),44)
Carbon foam AGM
Firefly makes the Oasis (AGM) battery with carbon foam. Claimed benefits are:
- increased current acceptance
- Absorption stage required only 1x/month or so rather than every day or so. Since Absorption stage is long-duration, this can cut down charging time considerably.
Carbon Flooded Lead Acid
Some manufacturers attempt to get around the Partial State of Charge limitations of lead chemistries by using carbon in some form. The idea is that the addition of carbon increases the internal conductivity of the negative plate under challenging conditions, minimizing hard sulfation that can form in PSOC scenarios.
In the milder form, carbon is added to the negative plates:
Battery manufacturers have begun including high purity conductive graphite in the negative active material of their batteries. They have found that this type of carbon helps to maintain the essential active material conductivity that helps to control sulfation.45)
- Rolls calls this “Advanced NAM”46) and claims 15% faster charging, increased capacity, and increased cycle life. They state that this type of battery may have higher endAmps due to less internal resistance.47)
Lithium chemistries
Lithium battery banks are lighter, more tolerant of abuse, and have higher energy density than lead-acid batteries. The main drawback is price. See the Lithium batteries page.
Lithium banks come in three main forms:
- “drop-in” batteries that are the same size and general voltage range as the lead batteries they replace. Example: Battle Born BMS is built in.
- DIY banks, often “bare” cells 3.2v cells in 4S configuration, with or without BMS. These are not the same size or shape as lead batteries, and require a moderate amount of knowledge to use without blowing yourself up.
- Manufactured complete banks that do not mimic the physical shape of lead batteries
BMS
Because of the very high energy density and sensitivity to temperature and voltage extremes, most Li banks are equipped with a Battery Management System (BMS) which monitors and controls the bank and the cells in it.
Depending on the BMS, features may include:
- protection from overcharging individual cells
- “top balancing” cells, getting cell voltages to match when fully charged
- protection from over-discharge
- protection from excess current in charging and/or discharging
- prevention of charging when temps are too low52)
LiFePO4
LiFePO4 drop-ins like Battle Born and SOKhave moved to their own page.
LiFePO4 DIY info can be found on on Will Prowse's pages about cells and BMS, and in this distillation of a 10-year thread on the Crusisers & Sailing forum.
Non-LiFePO4 lithium-ion
Non-LiFeP04 Li-ion [called “li-ion” hereafter] are usually built in 3S configuration and so run lower voltages than LFP or lead. Usable cell voltage is 4.2v - 3v, yielding bank voltage of 12.6v - 9v.53) This lower voltage may trip Low Voltage Disconnect on inverters or refrigerators.
There are hobbyists who build 4S packs and undercharge the cells to only 3.7v. This gives an operating range of 14.8v - 12v, a much better fit for nominal 12v systems. The downside is this configuration only uses 58% of the cells' capacity and will require more cells to achieve the same amount of Ah. The cells could be fully charged then the output regulated back to more normal 12v voltage ranges.
7S builds make a decent 24v bank. They are 29.4v fully charged and 21v discharged, compared to lead acid's 29.6v max voltage and 24.2v 50% DoD cutoff. Discharging 7s li-ion to 24v54) could help avoid LVD, making 35% of the cells' capacity unusable. 24v banks in general could preclude alternator charging, however.
Pro:
- About half the cost of LFP for the same Ah capacity
- widely available
Con:
- overcharging or physical damage can cause a runaway condition (ie fire)
- voltage mismatch of 3S to nominal 12v systems



